画像をダウンロード greenhouse effect global warming concept map 222197
Concept Map 910 Physics els724com > 910 Physics > Light Light Concept Map Open & Print Concept Map & Glossary Print Glossary CardsGlobal warming global warming Feedback mechanisms and climate sensitivity There are a number of feedback processes important to Earth's climate system and, in particular, its response to external radiative forcing The most fundamental of these feedback mechanisms involves the loss of longwave radiation to space from the surface Since this radiative loss increases with The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include water vapor,
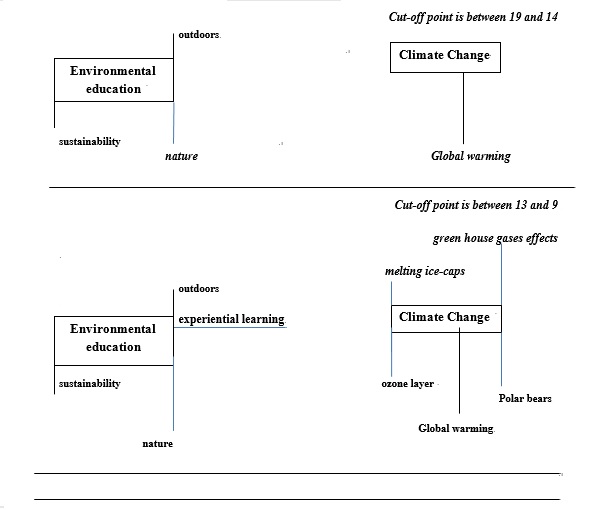
Cognitive Structures Of University Students About Environmental Education Climate Change And Consumption
Greenhouse effect global warming concept map
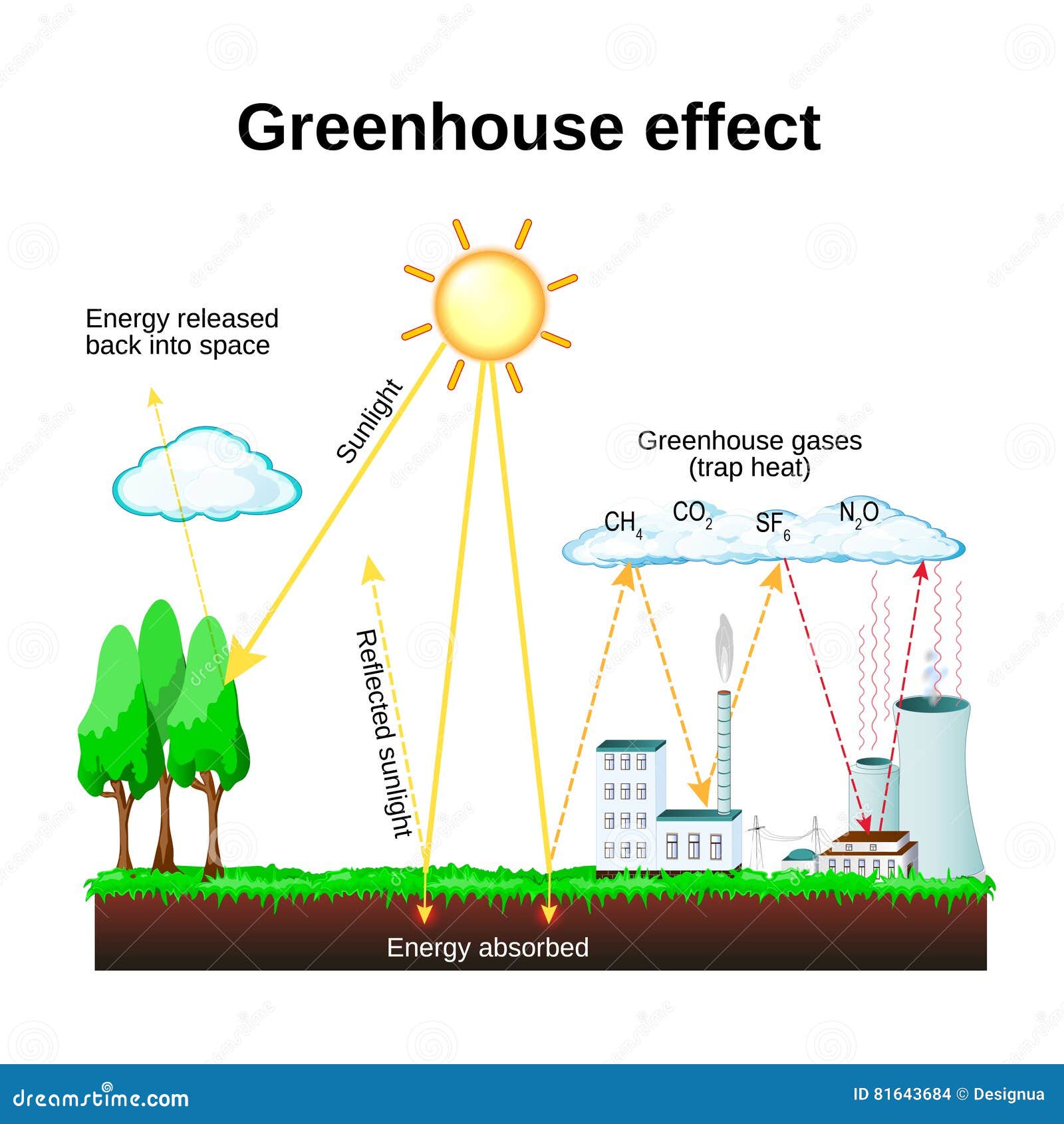
Greenhouse effect global warming concept map- Global warming is the longterm warming of the planet's overall temperature Though this warming trend has been going on for a long time, its pace has significantly increased in the last hundred years due to the burning of fossil fuels As the human population has increased, so has the volume of fossil fuels burned Fossil fuels include coal, oil, and natural gas, and burning The "greenhouse effect" is the warming that happens when certain gases in Earth's atmosphere trap heat These gases let in light but keep heat from escaping, like the glass walls of a greenhouse
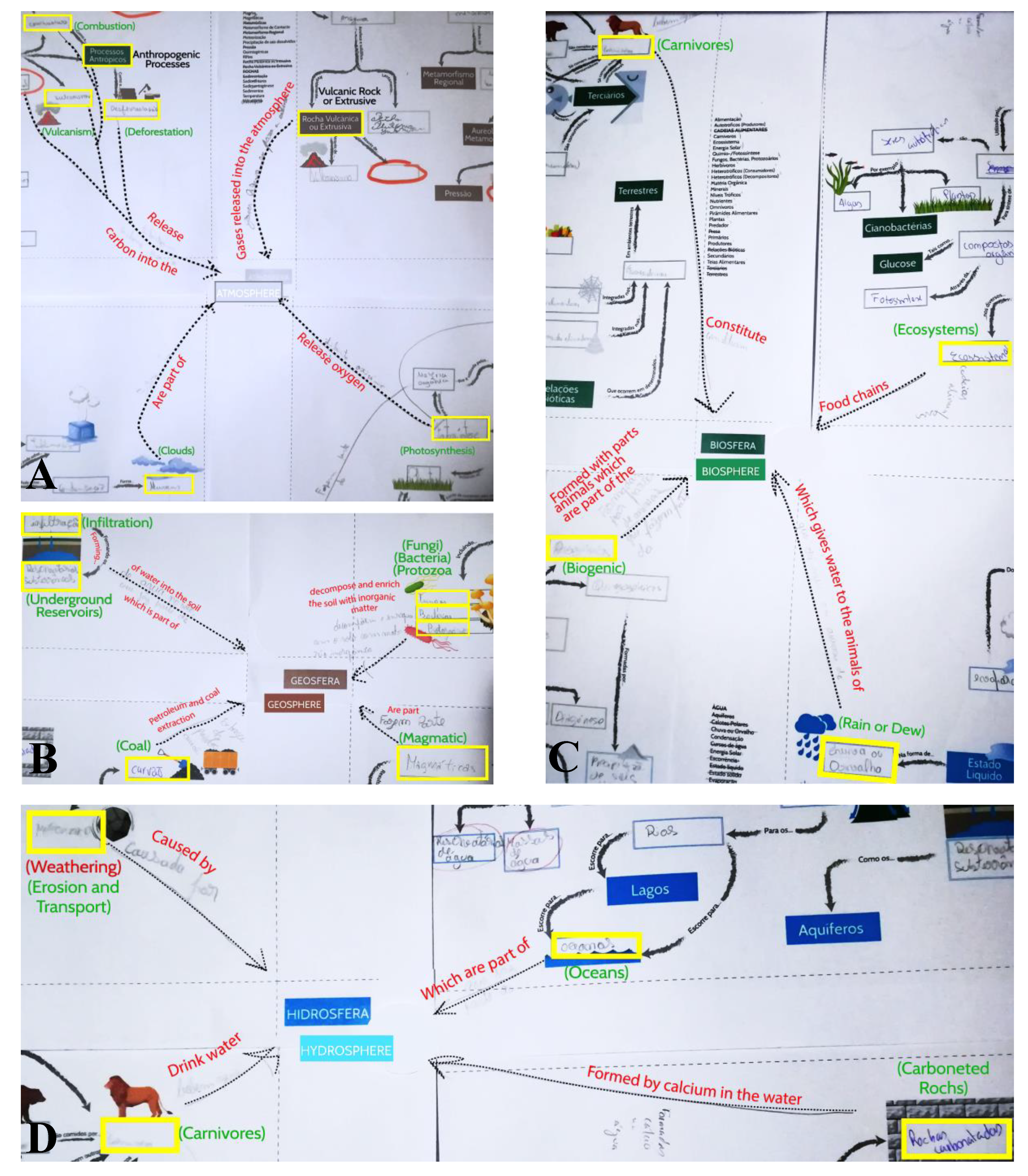



Geosciences Free Full Text Improved Concept Map Based Teaching To Promote A Holistic Earth System View Html
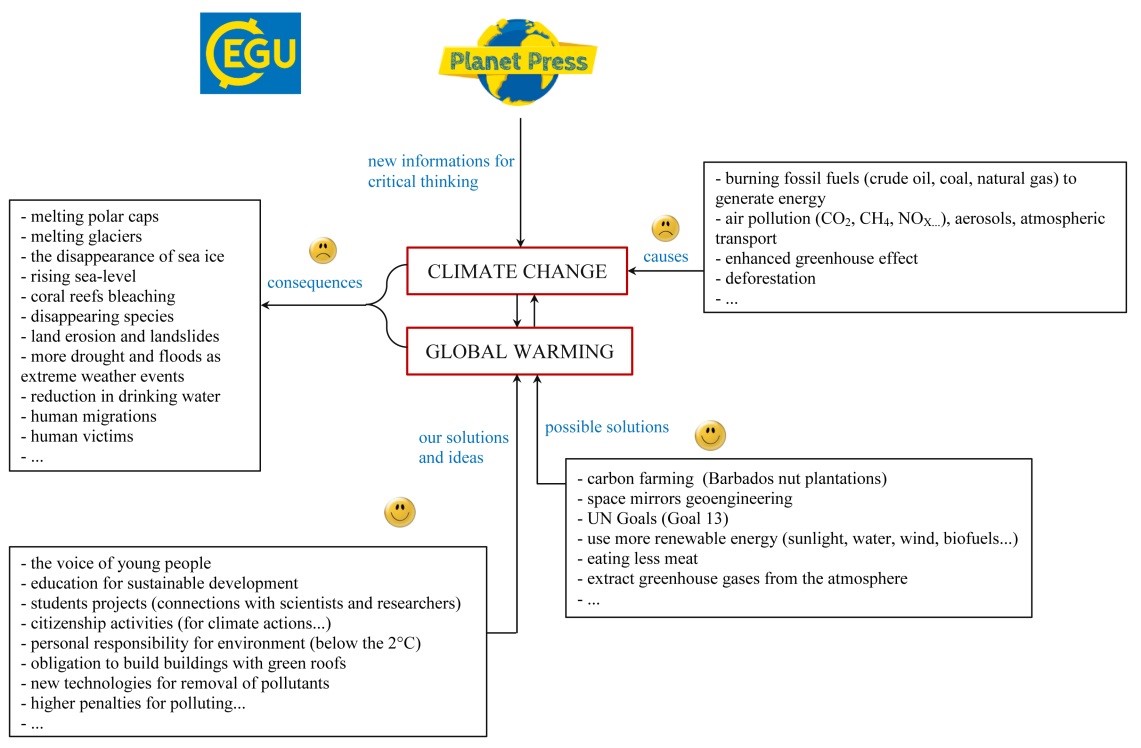
Humans can take action 1 a Sunlight warms the planet Sun is primary energy 2 c Greenhouse effect Climate is complex 3 b The Greenhouse effect supports the water cycle and makes life possible 4 f Evidence is that human impacts are playing an increasing role in climate change Climate is variableChanges in flower and plant blooming timesHuman action is causing an increase in global temperature For that reason, the greenhouse effect, far from being our great ally as was the case in the past, is now a risk to our survival The flooding of coastal cities, the desertification of fertile areas, the melting of glacial masses and the proliferation of devastating hurricanes are just some of the main consequences
Download this Vector Of Saving The Planet About Global Warming, Global, Warming, Earth transparent PNG or vector file for free Pngtree has millions of free png, vectors and psd graphic resources for designersThis step uses each gas's 100 year global warming potential, which measures how much a given amount of the gas is estimated to contribute to global warming over a period of 100 years after being emitted Carbon dioxide is assigned a global warming potential equal to 1 This analysis uses global warming potentials from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's (IPCC's)Water vapour is a potent greenhouse gas, thus causing more warming;
Global warming or climate change is the rising of the earth's average temperature day by day caused by the presence of different gases along with carbon dioxide at high levels in the earth's atmosphere #global warming #greenhouseeffect #climatechange #carbondioxideIts short lifetime in the atmosphere keeps its increase largely in step with warming Thus, water vapour is treated as an amplifier, and not a driver, of climate change Higher temperatures in the polar regions melt sea ice and reduce seasonal snow cover, exposing a darker ocean and land surface that can absorbIn terms of the net increase in the greenhouse effect due to humanproduced greenhouse gases, Such complications are often dealt with through the concept of global warming potential (GWP), which takes into account both the radiative properties of a particular greenhouse gas molecule and the lifetime that such a molecule typically has in the atmosphere, once emitted In



How To Create An Essay Outline Here Are The Basics
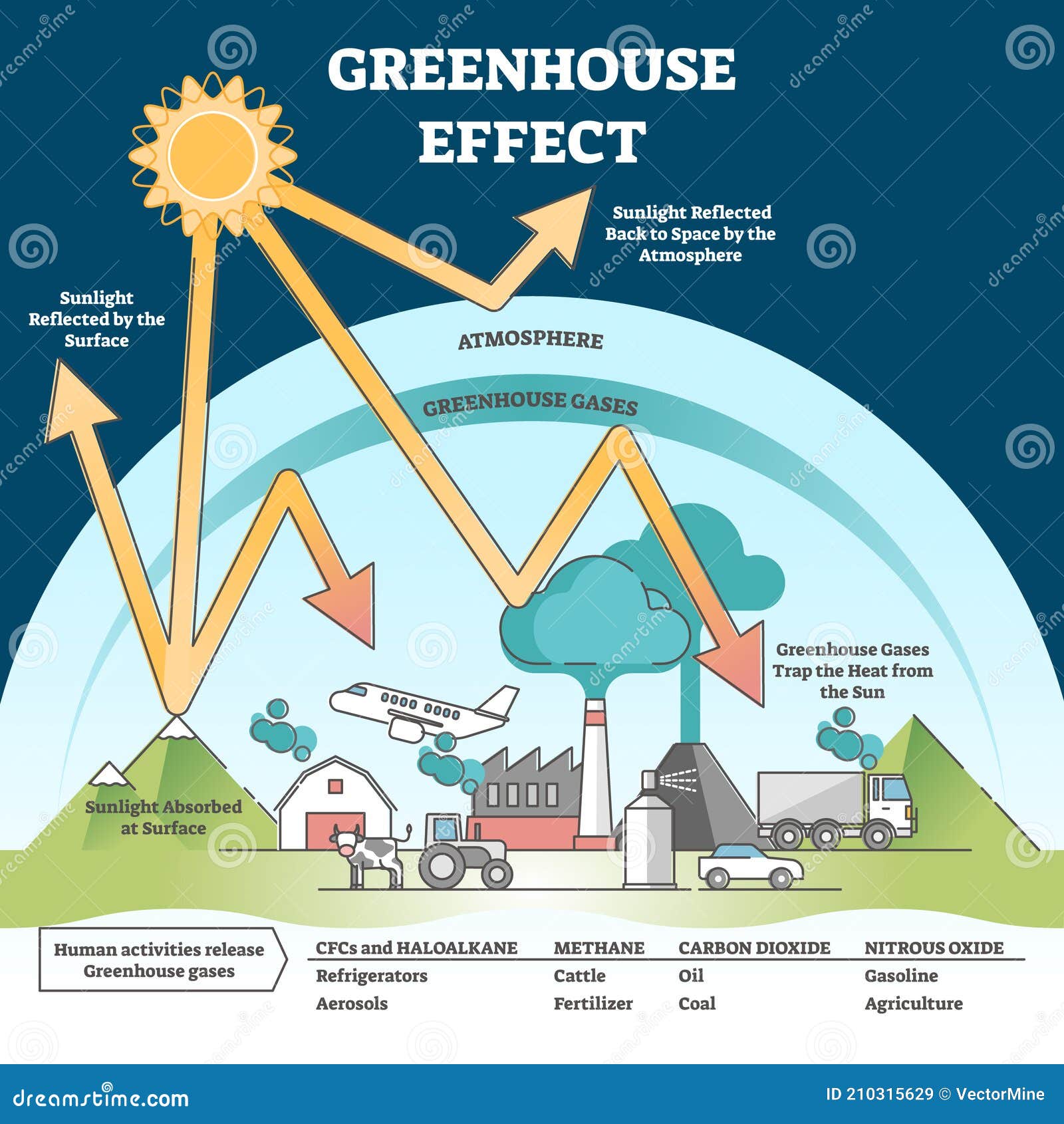



Greenhouse Effect And Climate Change From Global Warming Outline Concept Stock Vector Illustration Of Solar Planet
Global warming can result in many serious alterations to the environment, eventually impacting human health It can also cause a rise in sea level, leading to the loss of coastal land, a change inReleased by human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, are warming the Earth The mechanism commonly known as the ?greenhouse effect?GLOBAL WARMING EFFECTS The issue of global warming has been transformed from one of concern for a small group of scientists to an item on the agenda board of world leaders As an aid to thinking about the many interconnections of this topic the technique of a "future wheel" can be used One of the initiators of this technique back in the 1990s was the Acid Rain Foundation



Fullick H Climate Change Cmap What Is Climate Change
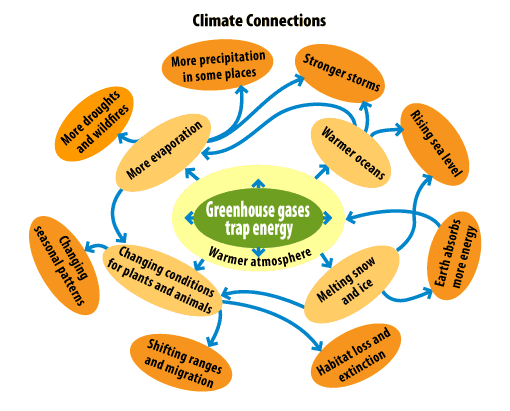



Climate Concepts A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
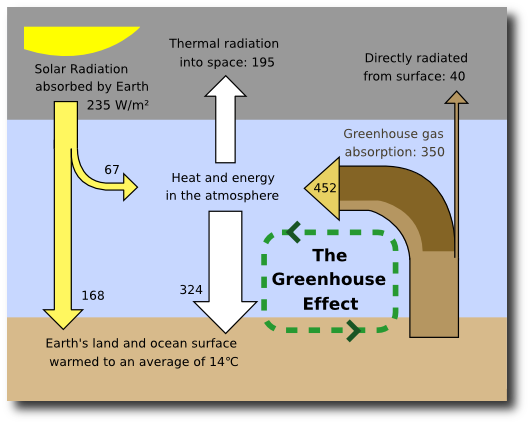
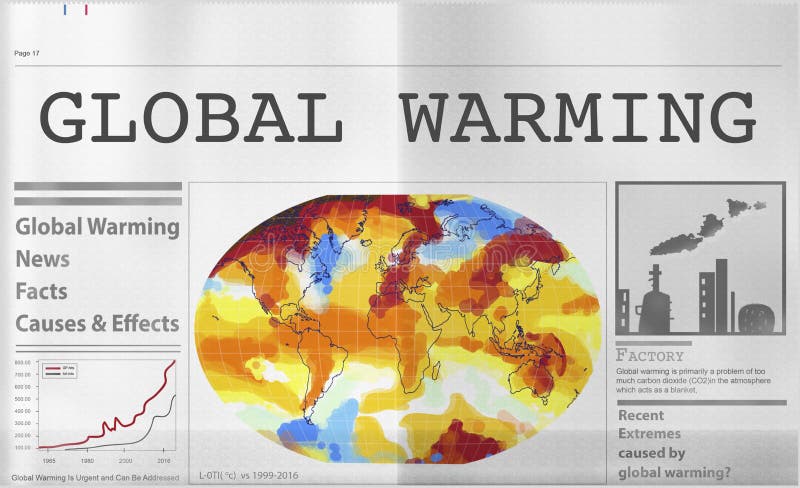
Greenhouse Effect Shown above is an Infrared Map of the Earth Red areas represent regions of high heat retention in the atmosphere This is an equatorial band because that is where the atmosphere has the most water vapor The earth has a natural greenhouse effect due to trace amounts of H 2 0 and CO 2 that naturally occur The enhanced greenhouse effect refers to the Describe the greenhouse effect and global warming Explain the concept of climate change Consider the effects of climate change on extreme weather Recognize ways that they can lower their impact on the environment at home Educational Standards Each TeachEngineering lesson or activity is correlated to one or more K12 science, technology, engineering or mathGlobal warming is the unusually rapid increase in Earth's average surface temperature over the past century primarily due to the greenhouse gases released as people burn fossil fuels The global average surface temperature rose 06 to 09 degrees Celsius (11 to 16° F) between 1906 and 05, and the rate of temperature increase has nearly




Climate Change Concept Map By Anupriya Mishra



Shauna Bassett Climate Change Concept Map 1st Submission
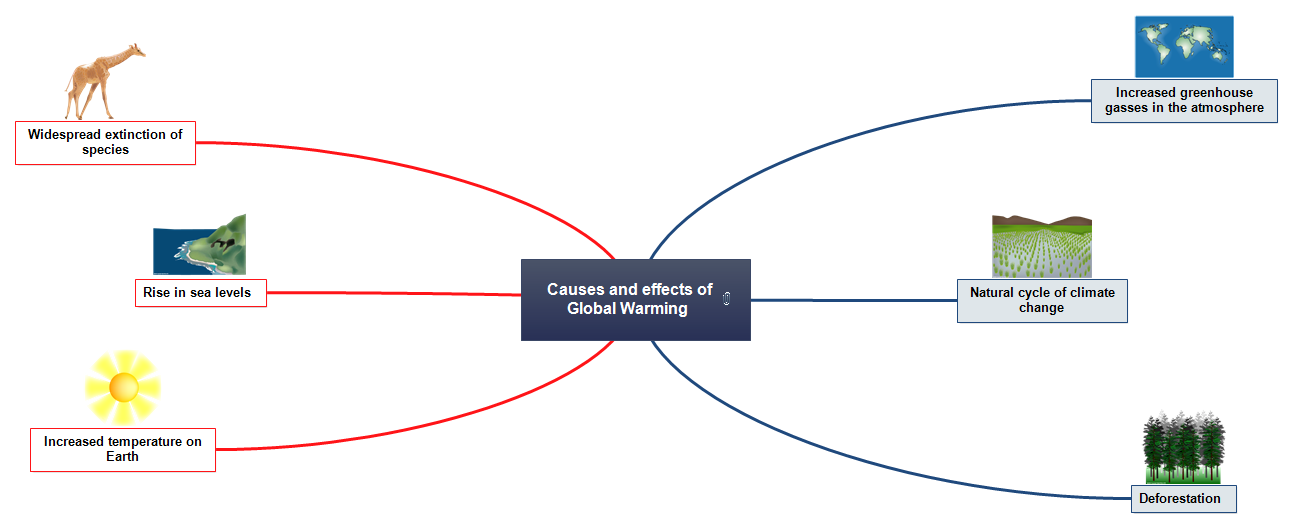
Anthropogenic global warming is a theory explaining today's longterm increase in the average temperature of Earth's atmosphere as an effect of human industry and agriculture For well over a century, scientists have been concerned that as the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere increases, so will the planet's capacity to retain heat Global climate change refers to the average longterm changes over the entire Earth These include warming temperatures and changes in precipitation, as well as the effects of Earth's warming, such as Rising sea levels;The greenhouse effect Without greenhouse gases in its atmosphere , the Earth would be about 18°C colder on average than it is now That would make it too cold to support life as we know it




Effects Of Climate Change Wikipedia




Climate Change What Is It Understanding The Basic Facts About Global Warming
During the first week of the project, students will be introduced to the concept of global warming from a statistical perspective They will watch a simulation on the future affects of global warming and discuss scientific notation Students will also learn to effectively use the Internet as a research tool The class will collect temperature and climate data over a span of 128 years to answerStudents observe teacherled demonstrations, and build and evaluate simple models to understand the greenhouse effect, the role of increased greenhouse gas concentration in global warming, and the implications of global warming for engineers, themselves and the Earth In an associated literacy activity, students learn how a bill becomes law and they research global warming An increase in the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases produces a positive climate forcing, or warming effect From 1990 to 19, the total warming effect from greenhouse gases added by humans to the Earth's atmosphere increased by 45 percent The warming effect associated with carbon dioxide alone increased by 36 percent




Vocabulary Climate Change Concept Map
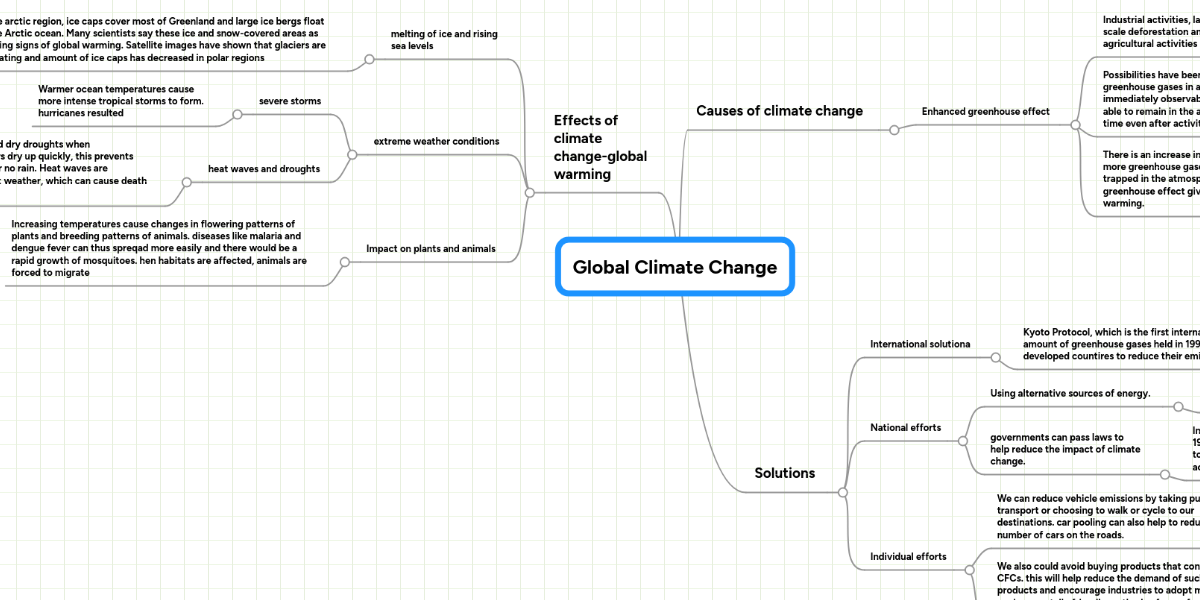



Global Climate Change Mindmeister Mind Map
Global warming definition, an increase in the earth's average atmospheric temperature that causes corresponding changes in climate and that may result from the greenhouse effect See more Graphic A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect Perhaps the most impressive of cloud formations, cumulonimbus (from the Latin for "pile" and "rain cloud") clouds form due to vigorous convection (rising and overturning) of warm, moist and unstable airMethane is the next of the greenhouse gases which has the biggest effect on global warming (15%) This is generated by activities such as livestock production, agriculture, sewage treatment, natural gas and oil distribution , coal mining, fuel use and is also given off from waste tips It lasts an average of 12 years in the atmosphere
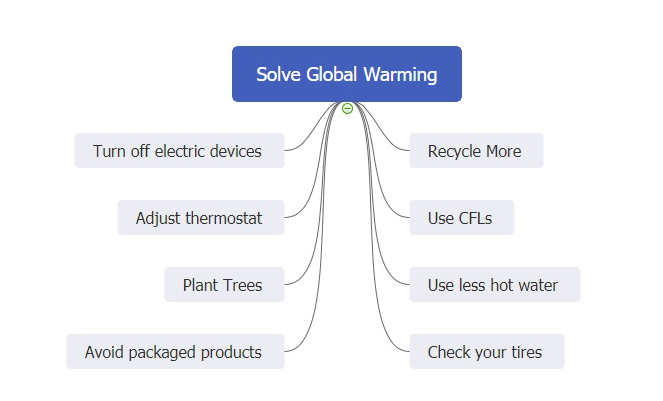



Global Warming Mind Maps Understand Climate Change Edrawmind



1
Ice melting at a faster rate than usual in Greenland, Antarctica and the Arctic; Greenhouse Effect 101 By increasing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, we're amplifying the planet's natural greenhouse effect and turning up the dial on global warmingHe said "global warming has reached a level such that we can ascribe with a high degree of confidence a cause and effect relationship between the greenhouse effect and the observed warming"4 Hansen's testimony was very widely reported in popular and business media, and after that popular use of the term global warming exploded Global change never gained traction in
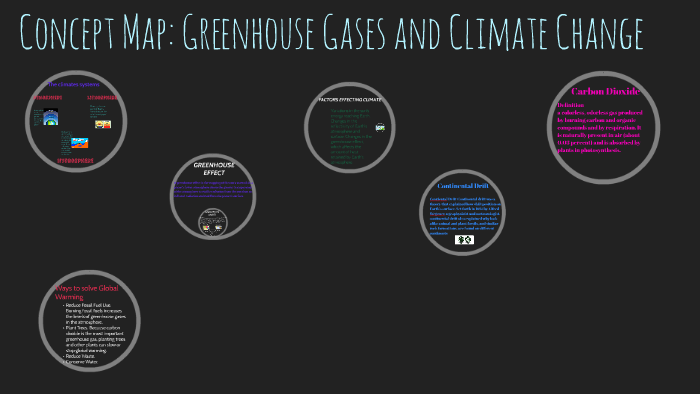



Concept Map Greenhouse Gases And Climate Change By Kimberly Hall
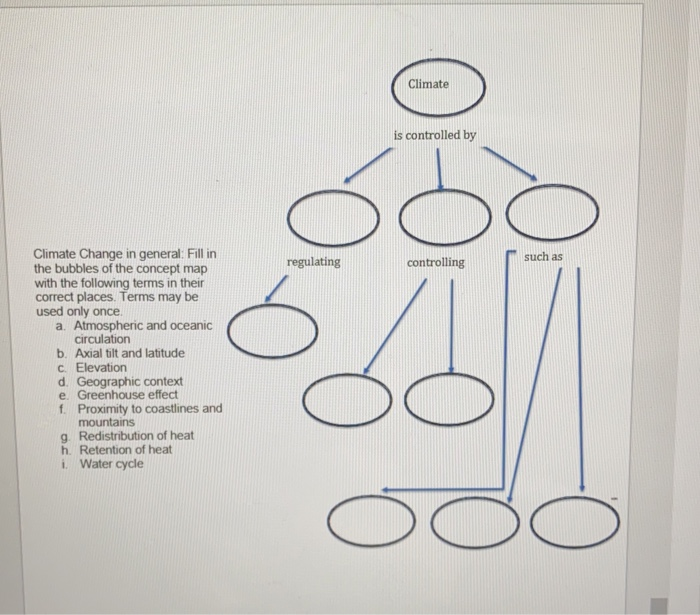



Solved Can Some One Please Help With This I Thougth I Had Chegg Com
Mind_map TZ Created with Raphaël 230 GLOBAL WARMING CONCEPT Global warming is a gradual increase in the overall temperature of the earth's atmosphere generally attributed to the greenhouse effect caused by increased levels of carbon dioxide, chlorofluorocarbons, and other pollutantsGlobally averaged, fine humanmade tropospheric aerosols may currently cancel about 50 % of the warming effect of humanmade greenhouse gases So far, though, the uncertainty range is large, stretching from roughly 10 to 100% Moreover, global averages are misleading Even if the global averages of aerosol and greenhouse gas forcing cancel, their different distributions may causeIs what makes the Earth habitable




26 5 The Thermosphere The Atmosphere Siyavula
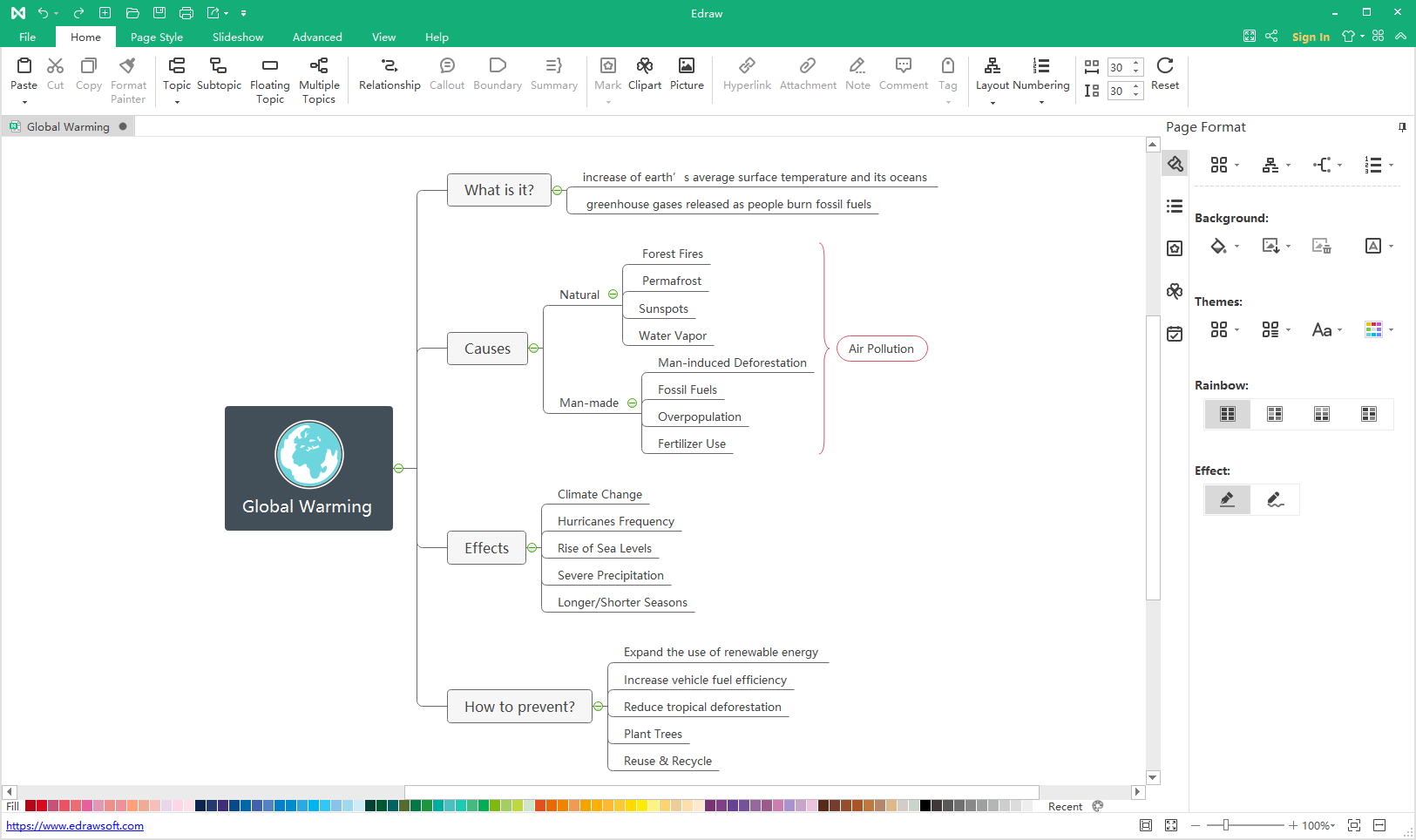



Global Warming Mind Maps Understand Climate Change Edrawmind
Greenhouse Effect Global warming describes the current rise in the average temperature of Earth's air and oceans Global warming is often described as the most recent example of climate change Grades 11, 12 Subjects Earth Science, Meteorology, Geography Contents 6 Images This lists the logos of programs or partners of NG Education which have provided or contributedShrinking mountain glaciers ; In this article we will discuss in brief about global warming and greenhouse effect Greenhouse Effect About 75% of solar energy reaching the earth is absorbed by the earth's surface Remaining energy is reflected back in the atmosphere The reflected energy is absorbed by some gases called as greenhouse gases Some of the greenhouse gases are water vapor,




Climate Change Definition Causes Effects Facts Britannica
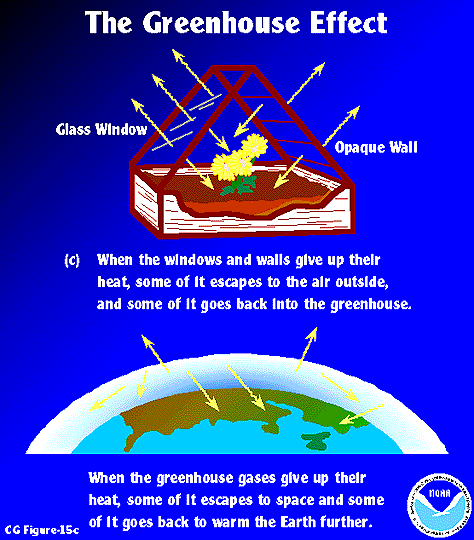



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
1861 Irish physicist John Tyndall shows that water vapour and certain other gases create the greenhouse effect "This aqueous vapour is a blanket more necessary to the vegetable life of England By the end of this century, their greenhouse effect alone would have contributed an additional 17°C global warming This is in addition to the newly quantified 08°C warming, coming from the extra CO 2 that would have resulted from damaged vegetation, meaning that temperatures would have risen 25°C overallGreenhouse gases have very different warming effects one tonne of methane does not have the same impact on warming as one tonne of CO 2Carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 e) attempt to convert the warming impact of the range of greenhouse gases into a single metric This is done by multiplying each gas by its 100year 'global warming potential' value the amount of warming
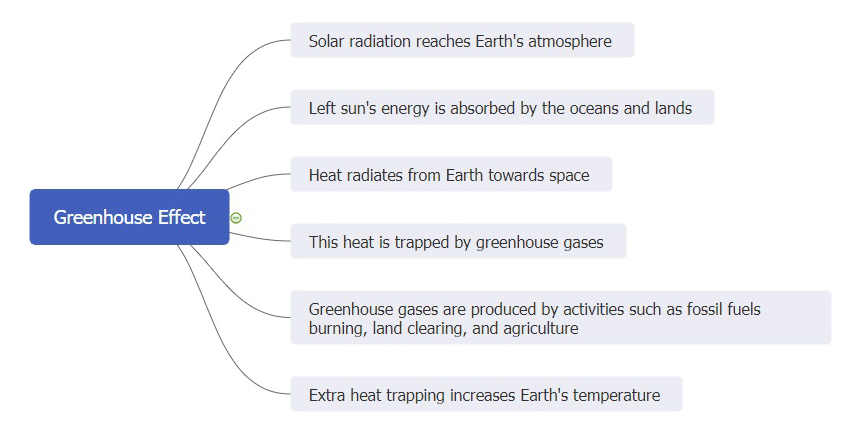



Global Warming Mind Maps Understand Climate Change Edrawmind



Mindmap Of The Greenhouse Effect Amp Global Warming By Luv Singh
Climate Change (Global Warming) Many climatologists believe that increasing atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide and other ?greenhouse gasses?TraceGas Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming Underlying Principles and Outstanding Issues Volvo Environmental Prize Lecture1997 This paper describes the developments that transformed the global warming problem from that arising solely from C02 increase to the tracegas greenhouse effect problem in which several nonCO2 gases, CFCs, CH4, N, 03 and others The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides Scientists have determined that carbon dioxide's warming effect




Bio Chapter Homework Flashcards Quizlet



Climate Change And Global Warming Introduction Global Issues
These characteristics are incorporated in the Global Warming Potential (GWP), a measure of the radiative effect (ie the strength of their greenhouse effect) of each unit of gas (by weight) over a specified period of time, expressed relative to the radiative effect of carbon dioxide (CO 2) This is often calculated over 100 years, though it can be done for any time period Gases with high Somewhere I picked up the concept that the greenhouse effect was caused by the absorption by certain gases of energy radiating from the earth's surface at specific wave lengths and reemitting that energy at the same wavelengths, but in all directions so that half of the energy reemitted is directed back towards earth This seem plausible to me because if the energy were




Geosciences Free Full Text Improved Concept Map Based Teaching To Promote A Holistic Earth System View Html



Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Stock Vector Illustration Of Ecology Greenhouse



Geolog Geotalk Sharing Geoscience With Kids And Educators




Aisha S Notebook Concept Mapping And Clustering




Concept Map C 10 Project Lead The Way Inc Civil Engineering And Architecture Ppt Download




Effects Of Climate Change Wikipedia




Educational Technology




The Effects Of Climate Change Part 3 And 4 Section 3 The Effect Of Climate Change Recap Over The Notes From The Last Day What Is The Difference Between Ppt Download



Causes And Effect Matchware Examples




The Concept Map Constructed According To Students Post Conceptions Of Download Scientific Diagram
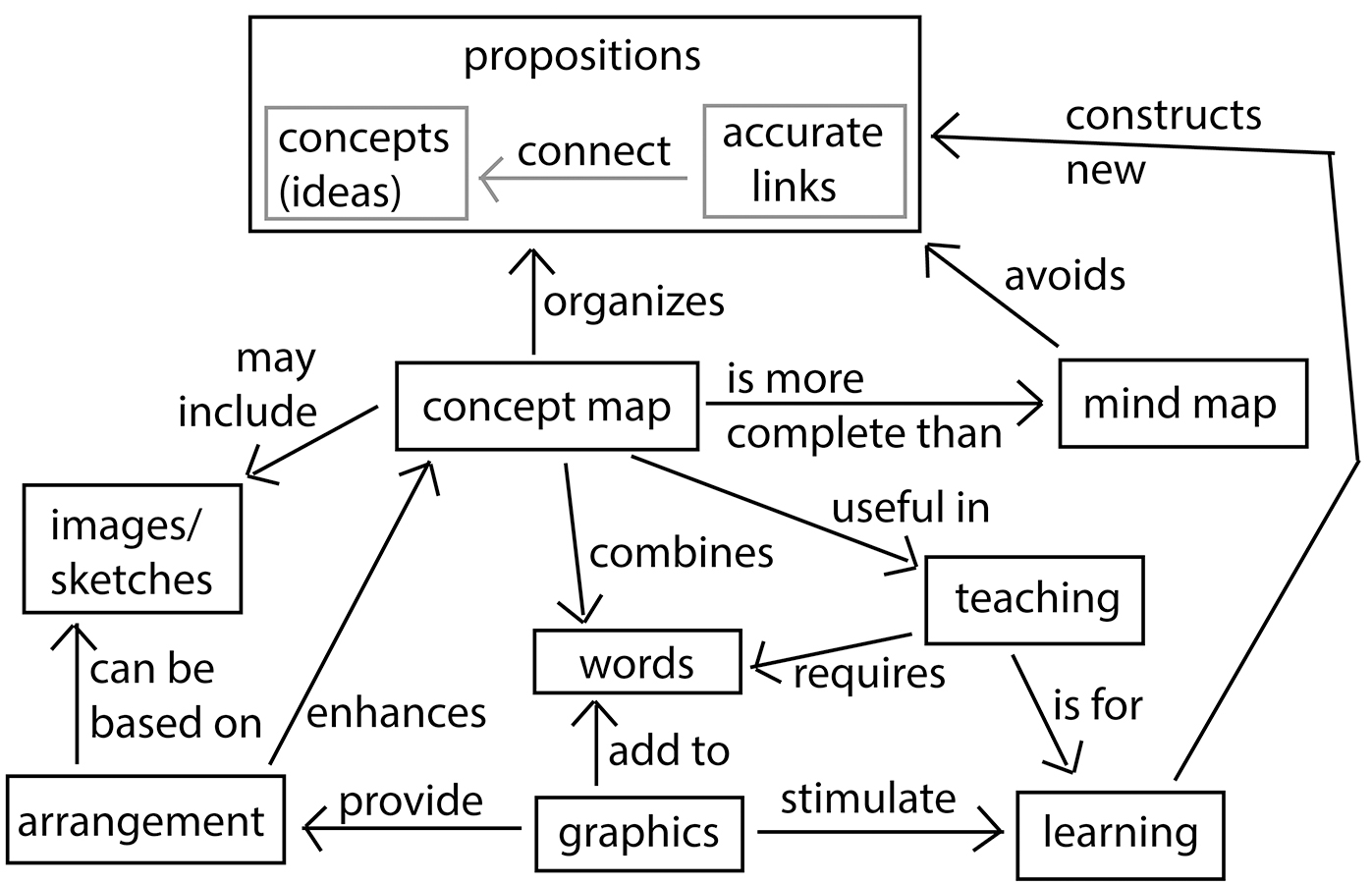



Concept Maps For Structuring Instruction And As A Potential Assessment Tool In A Large Introductory Science Course Nsta




Understanding What Students Know About Global Climate Change Conceptual Understanding Evaluation Using Concept Maps Based On Stacy Rebich Master S Thesis Ppt Video Online Download




Mind Map Global Warming And Green House Effect Arisara Pie The One And Only




Global Climate Change Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ck 12 Foundation




Global Climate Change Youtube
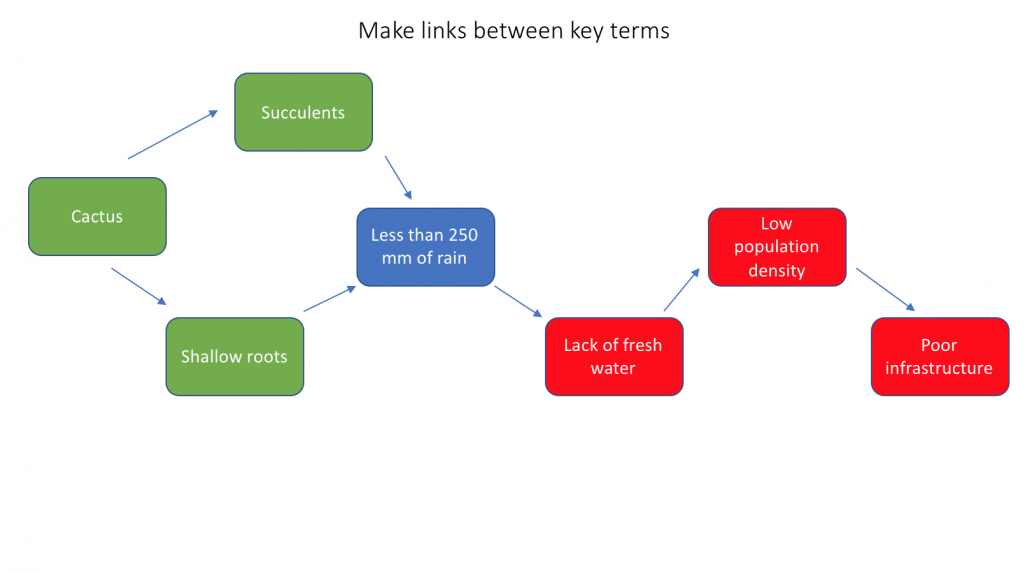



Concept Mapping Deserts Internet Geography
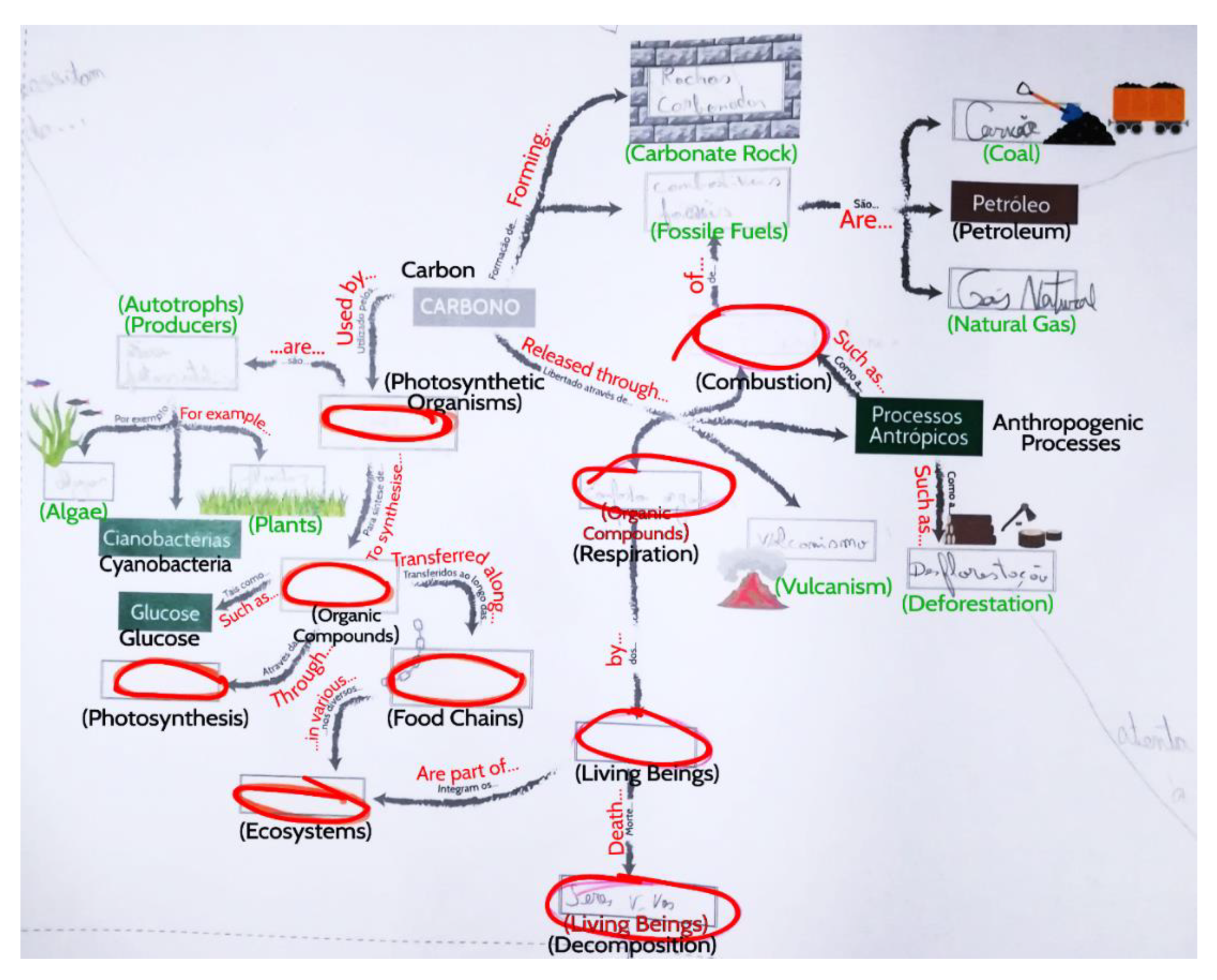



Geosciences Free Full Text Improved Concept Map Based Teaching To Promote A Holistic Earth System View Html
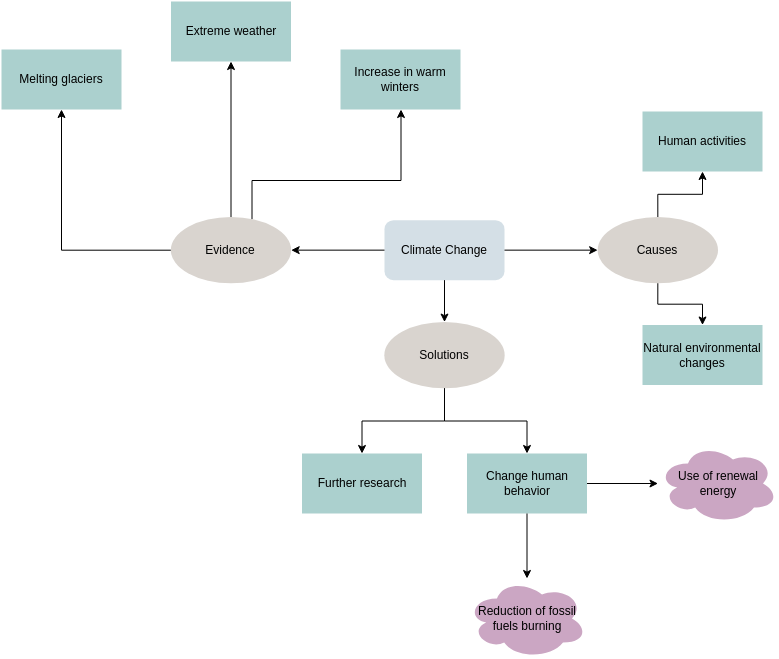



Climate Change Concept Map Diagram Template




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Climate Change And The Greenhouse Effect Worksheet Teaching Resources Efecto Invernadero Cambio Climatico Recursos Didacticos




Greenhouse Effect Abstract Concept Vector Illustration Global Warming Climate Change Cause Co2 Emission Rise Global Effect Greenhouse Gas Air Po Stock Vector Image Art Alamy



7 676 Greenhouse Effect Photos Free Royalty Free Stock Photos From Dreamstime



Ipads In K 8 Education Crazy For Concept Mapping




Visual Map Of Students Conceptions About Global Warming And Climate Change Download Scientific Diagram




Pdf An Exploration Of The Concept Map As An Interview Tool To Facilitate The Externalization Of Students Understandings About Global Atmospheric Change Semantic Scholar



Climate Change Concept Map Diagram Template



Combating Global Warming Mind Map Noaa Climate Gov



Champagne Final Global Warming
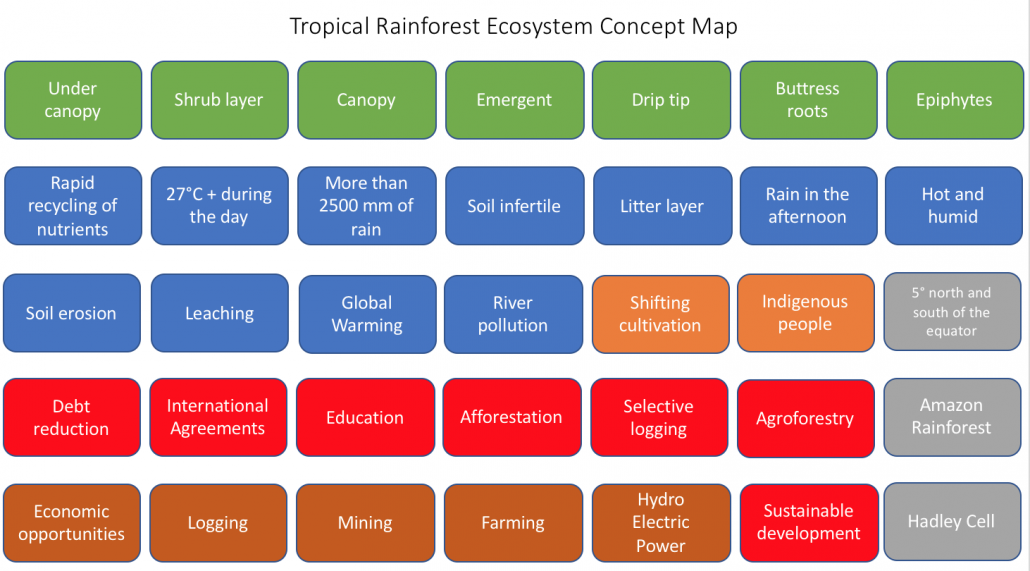



Concept Mapping Tropical Rainforest Internet Geography




10 Climate Change Maps The Climate Explained Gis Geography




Concept Map Concept Map Civil Engineering And Architecture Ppt Download



3
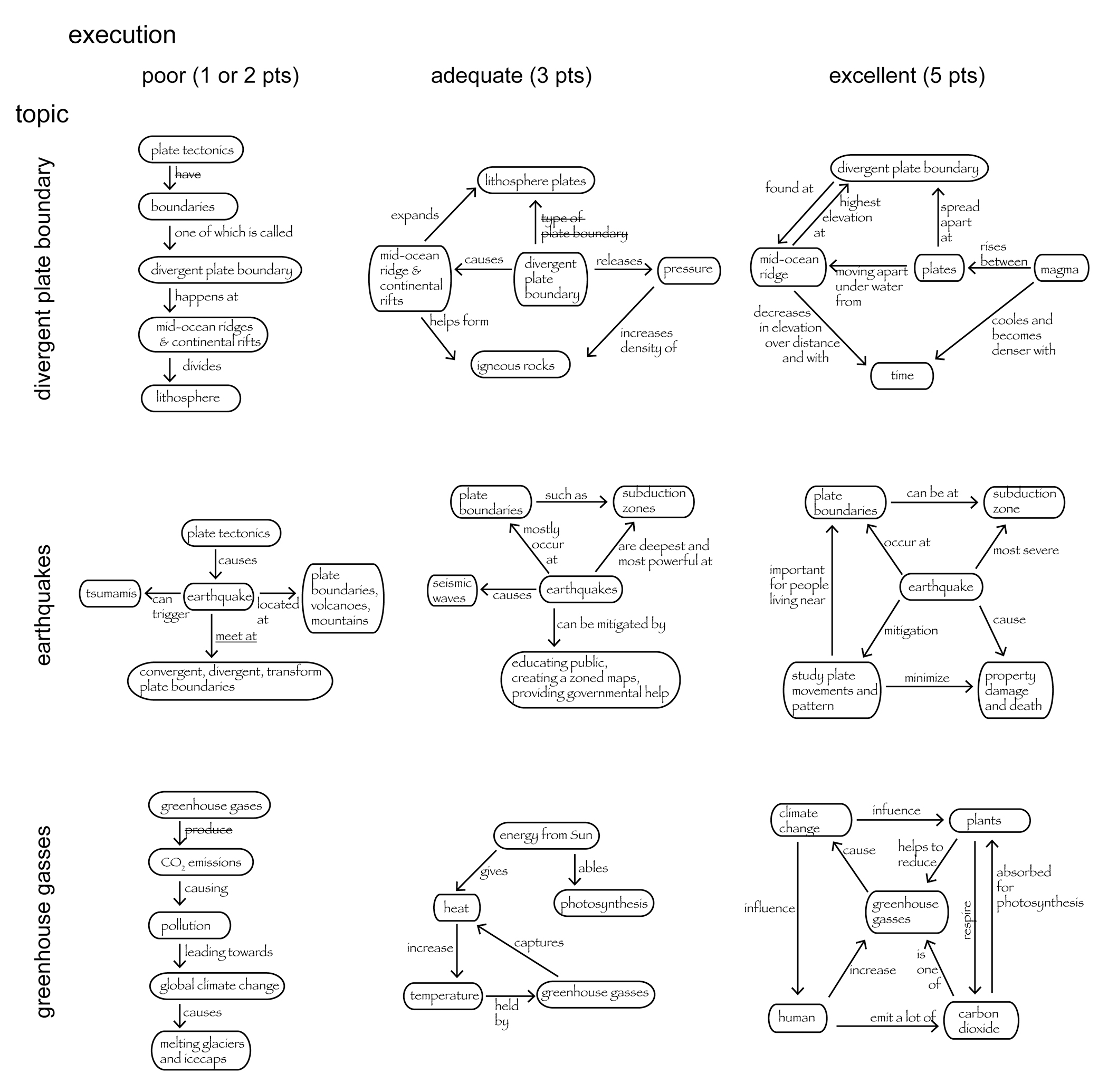



Concept Maps For Structuring Instruction And As A Potential Assessment Tool In A Large Introductory Science Course Nsta
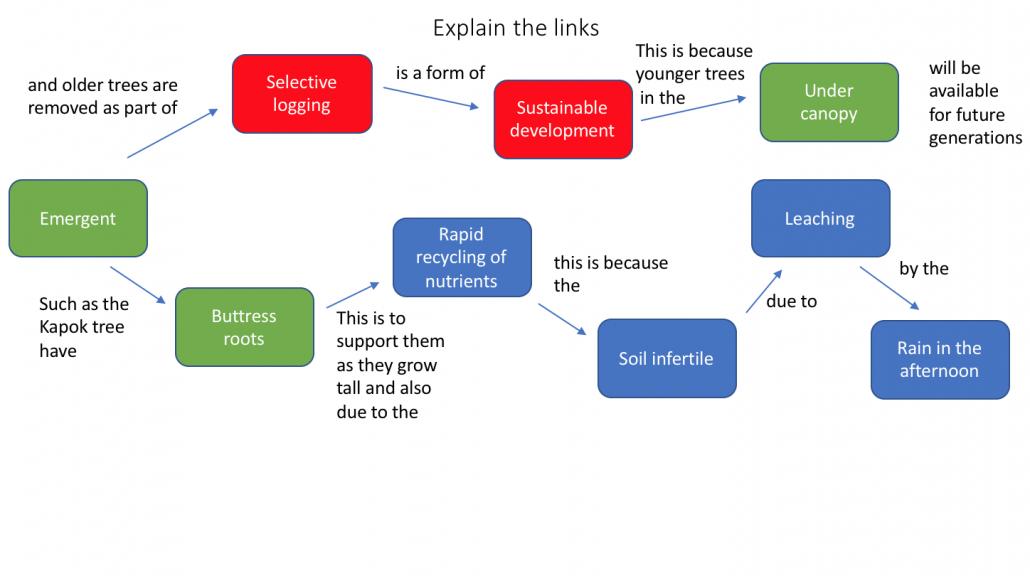



Concept Mapping Tropical Rainforest Internet Geography




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Concepts Videos And Examples




Climate Change Mind Map




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia



3




A Sample Climate Change Concept Map Expert Opinion Download Scientific Diagram




Abcs Of Climate Change Justearth




Pdf An Exploration Of The Concept Map As An Interview Tool To Facilitate The Externalization Of Students Understandings About Global Atmospheric Change Semantic Scholar




Global Warming 101 National Geographic Youtube




Climatechange Archives The Stem Discovery Campaign Blogthe Stem Discovery Campaign Blog




Cognitive Structures Of University Students About Environmental Education Climate Change And Consumption



1




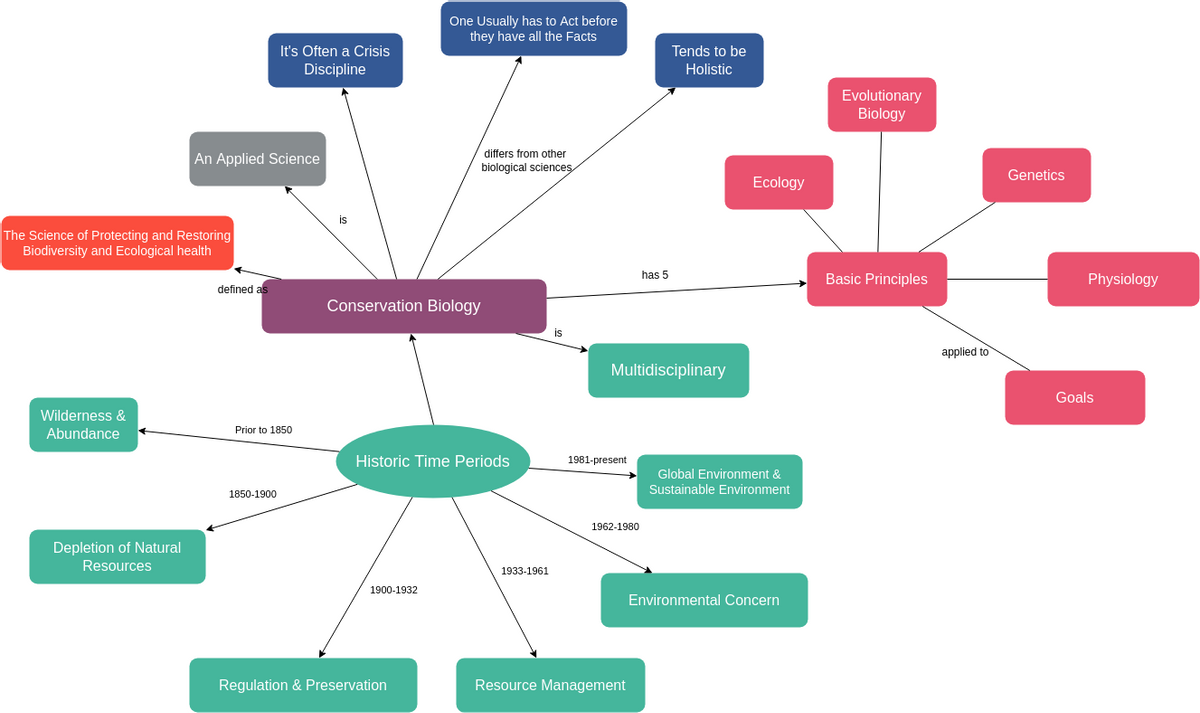
Concept Map Gw Pdf




Global Warming Pollution Greenhouse Effect Concept Stock Photo Alamy



Staging Rise S3 Amazonaws Com
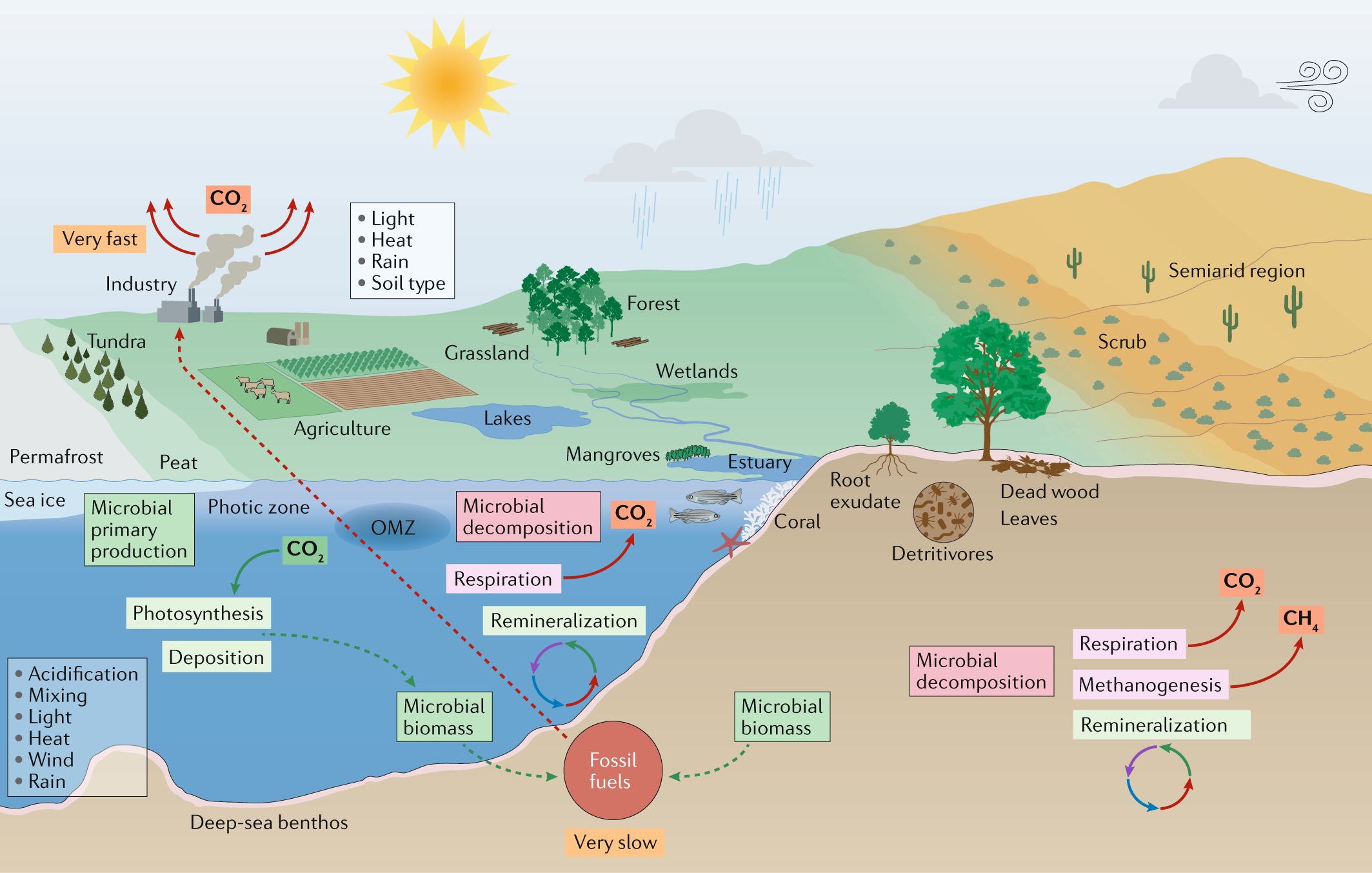



Scientists Warning To Humanity Microorganisms And Climate Change Nature Reviews Microbiology



Human Geography Mindmeister Mind Map
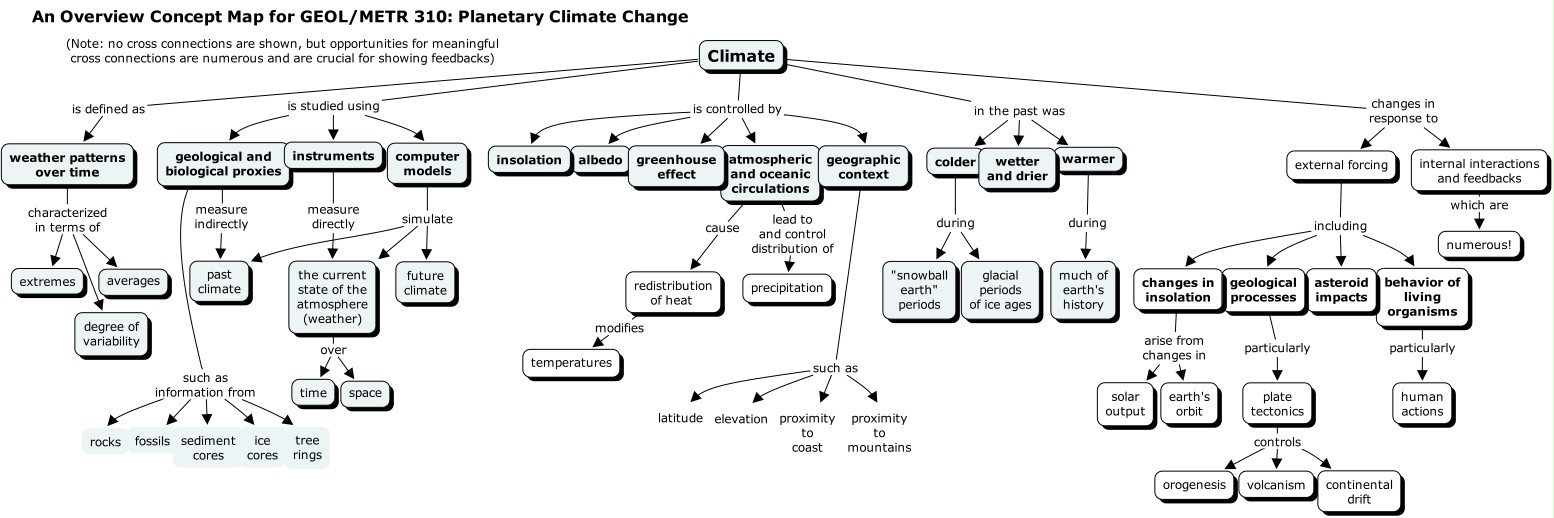



A Concept Mapping Assessment Of Climate Change Concepts
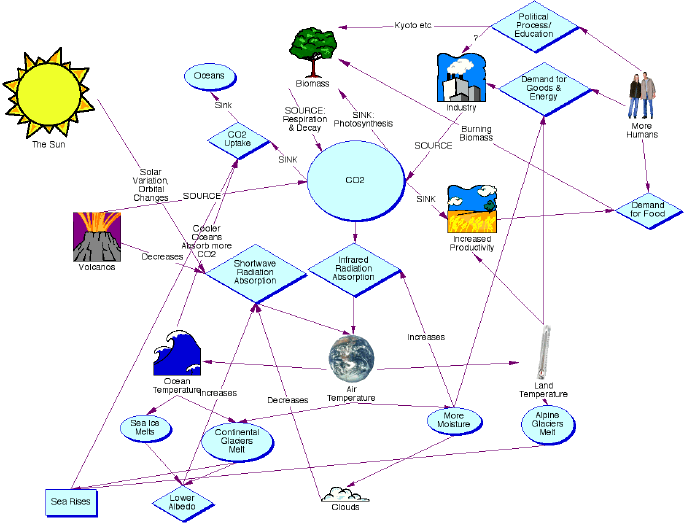



Climate Feedback Mechanisms And Human Response
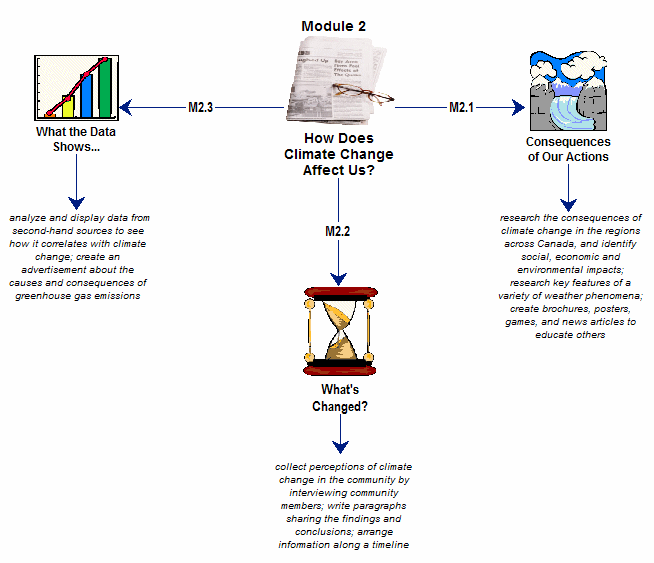



Climate Change Module 2 Concept Map
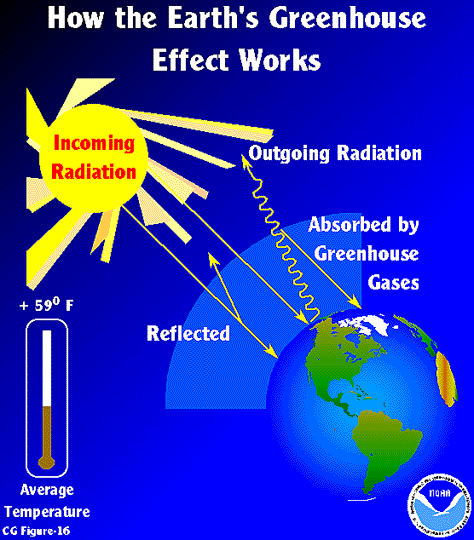



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Essential Question Why Are Soil Microbes Impacted By Human Activity Ppt Download
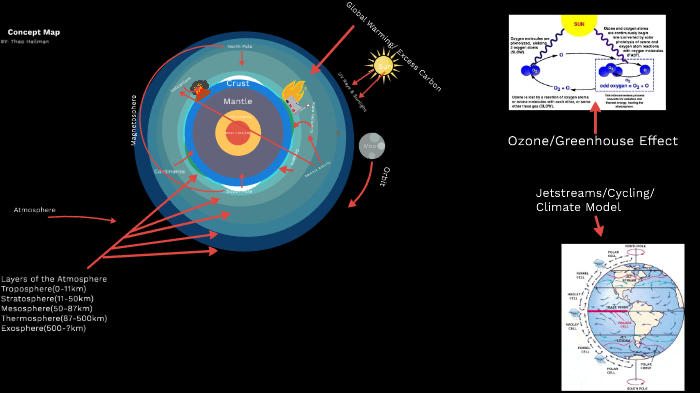



Planetary Concept Map By Theo Heilman
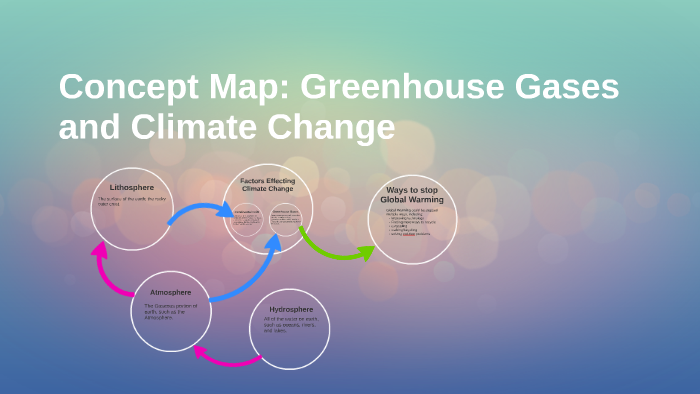



Concept Map Greenhouse Gases And Climate Change By Leroy Clark
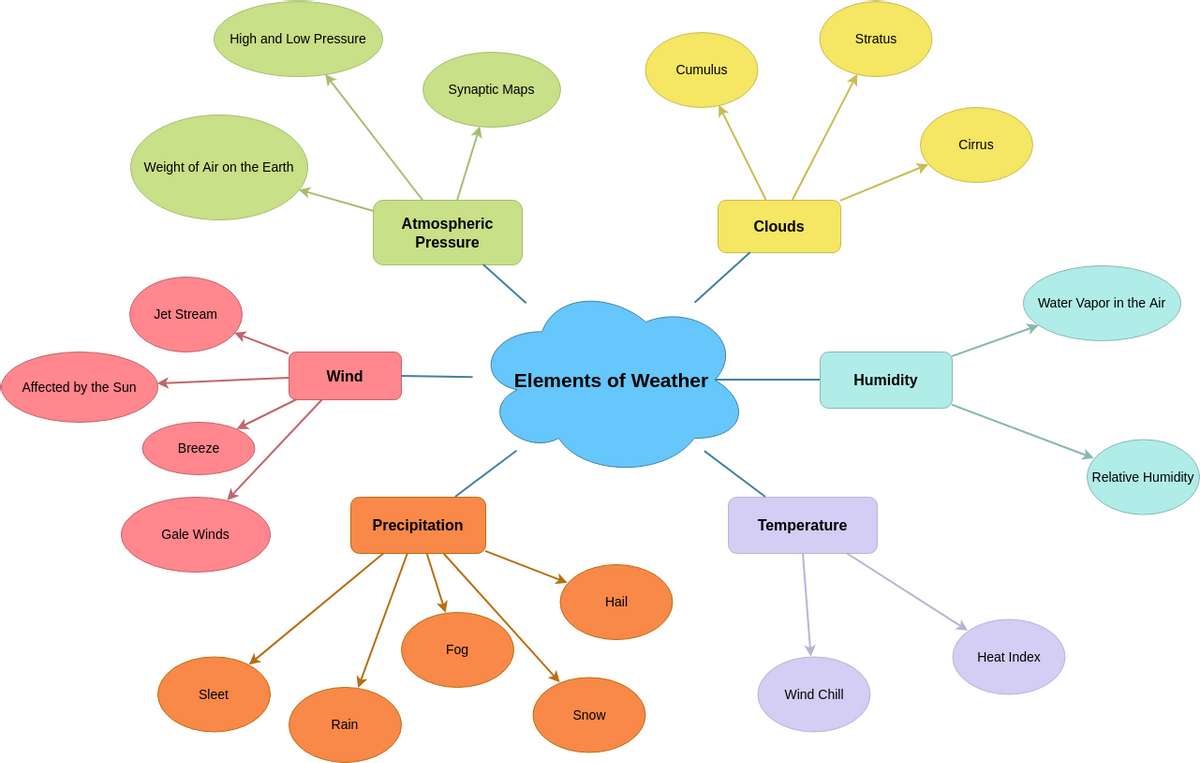



Climate Change Concept Map Diagram Template




Pdf An Exploration Of The Concept Map As An Interview Tool To Facilitate The Externalization Of Students Understandings About Global Atmospheric Change Semantic Scholar
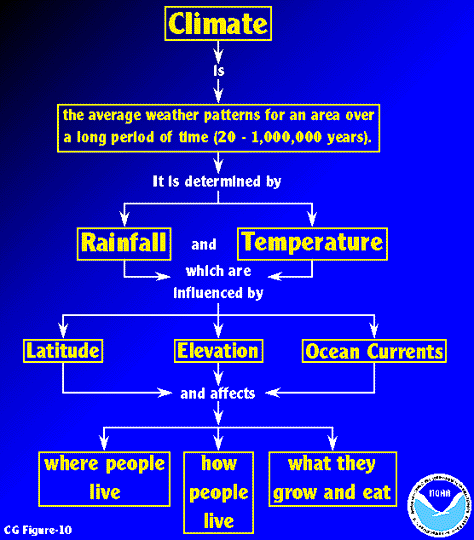



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
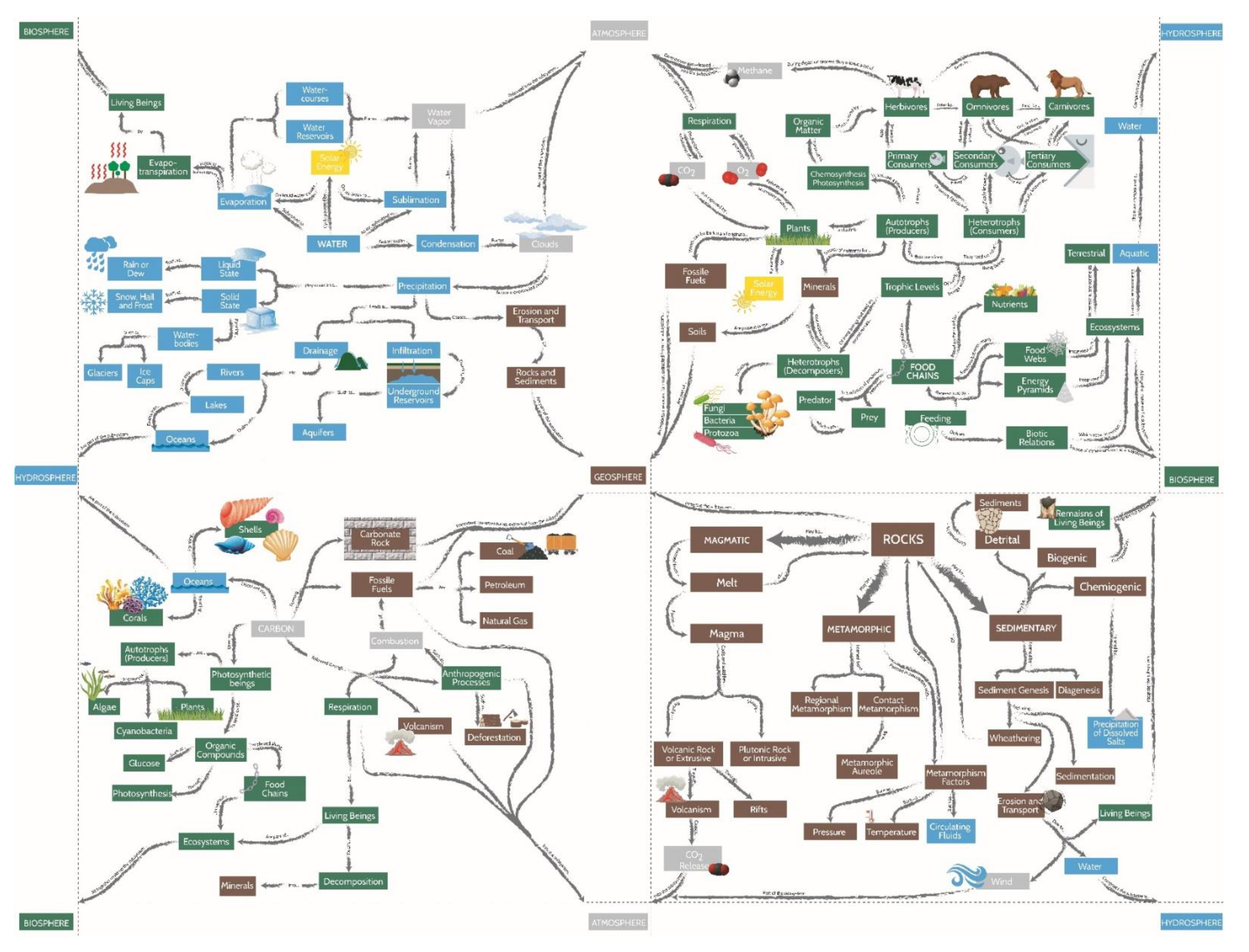



Geosciences Free Full Text Improved Concept Map Based Teaching To Promote A Holistic Earth System View Html




A Mind Map On Global Warming Mind Map Global Warming Climate Change Global Warming
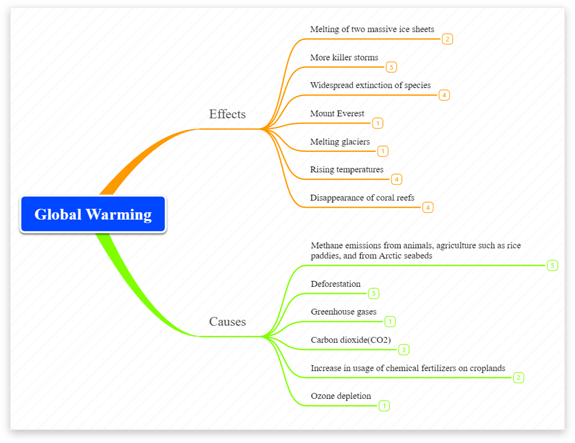



Mind Maps For Personal Development Mindomo Software




The Greenhouse Effect Mindmeister Mind Map
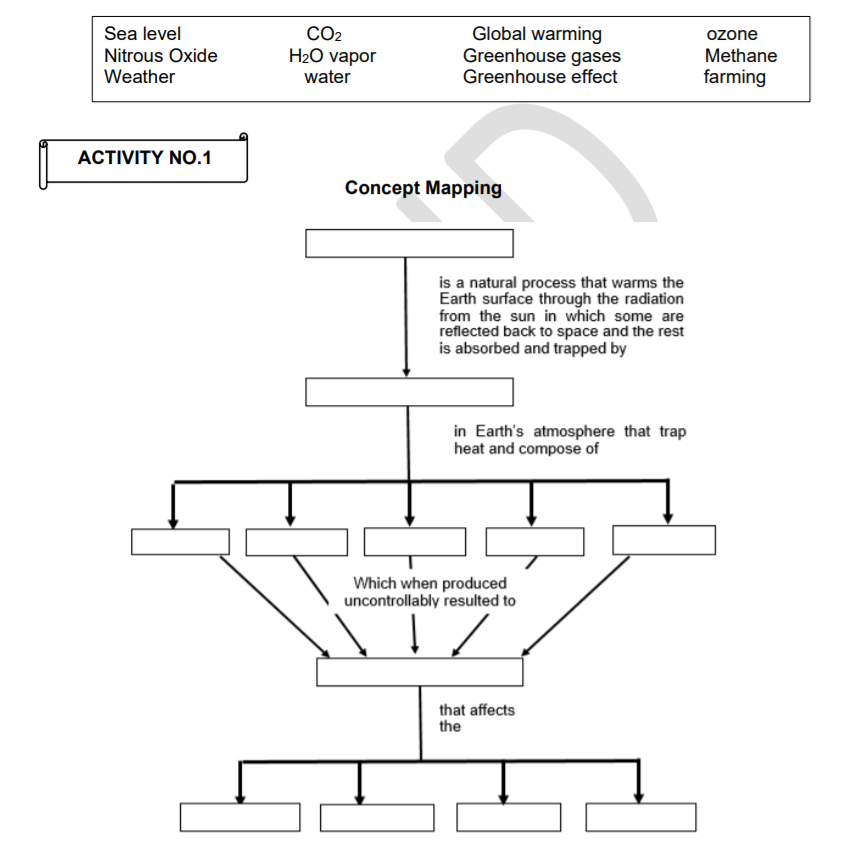



Answered Co2 H2o Vapor Global Warming Greenhouse Bartleby




Group E Concept Mapping Of Seminar Topics Wikienfk5



Climate Reality Building Leadership On Climate Change Educators




Global Warming Mind Map Global Warming Mind Map Art
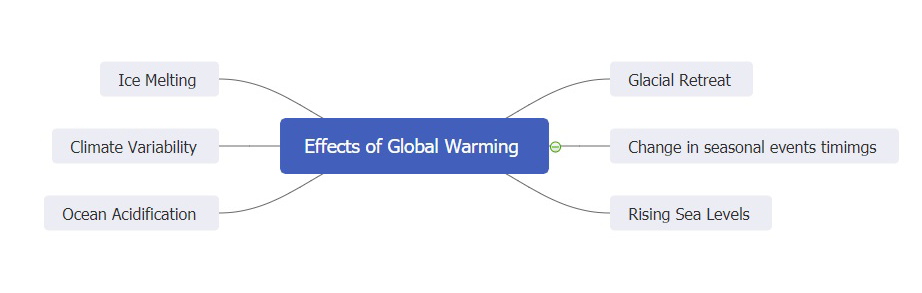



Global Warming Mind Maps Understand Climate Change Edrawmind
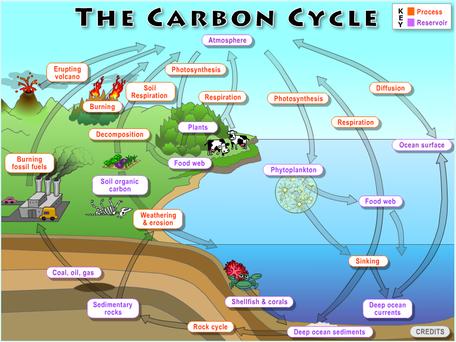



Climate And The Carbon Cycle Unit Overview




Example Concept Map For Atmospheric Ozone General Ozone Concepts Are Download Scientific Diagram
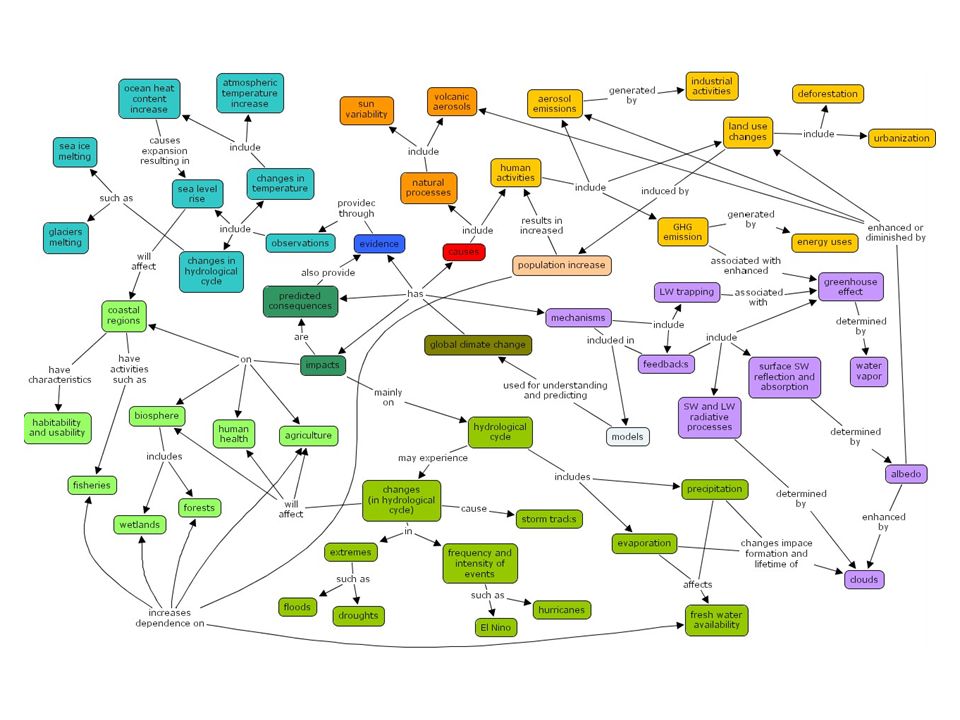



Understanding What Students Know About Global Climate Change Conceptual Understanding Evaluation Using Concept Maps Based On Stacy Rebich Master S Thesis Ppt Video Online Download




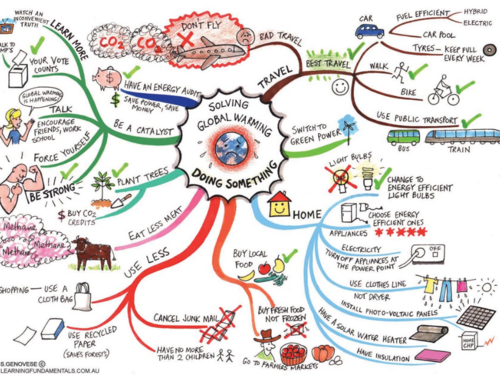
How To Help Solve Global Warming Impact Of Global Warming Mind Map Climate Change Effects




Composite Concept Map Of Causes Of Climate Change As Well As Positive Download Scientific Diagram




Bio Chapter Homework Flashcards Quizlet
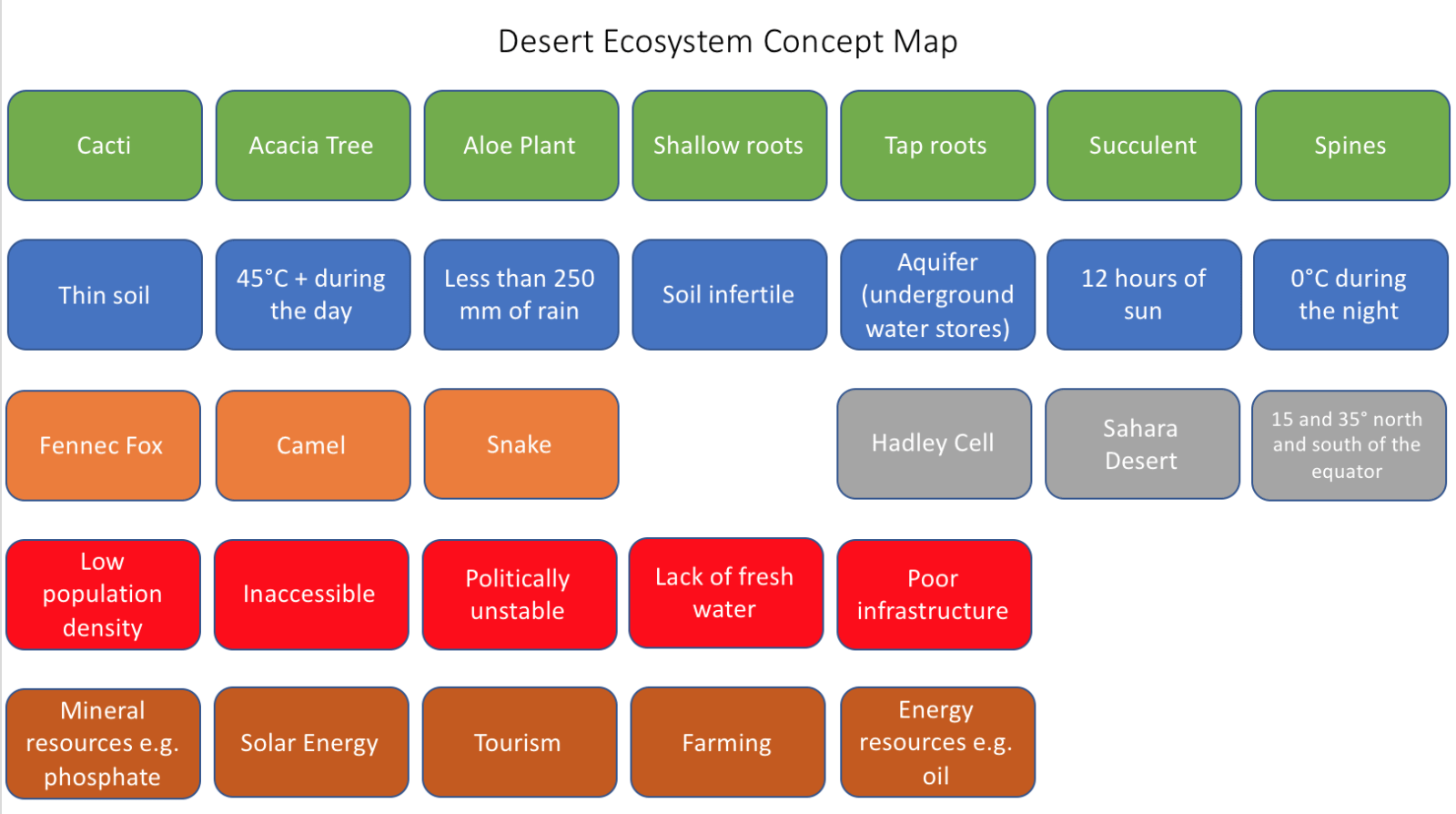



Concept Mapping Deserts Internet Geography
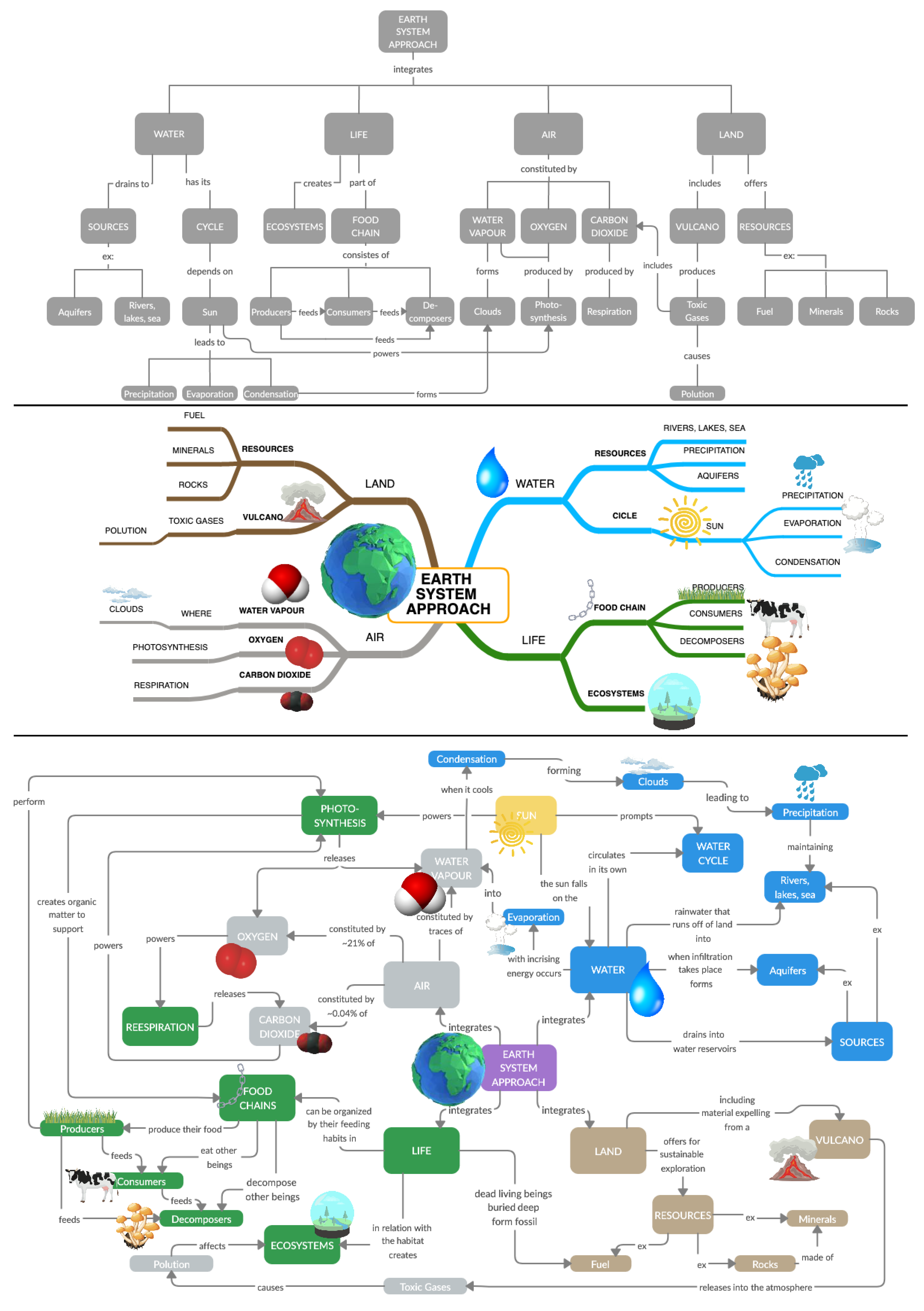



Geosciences Free Full Text Improved Concept Map Based Teaching To Promote A Holistic Earth System View Html
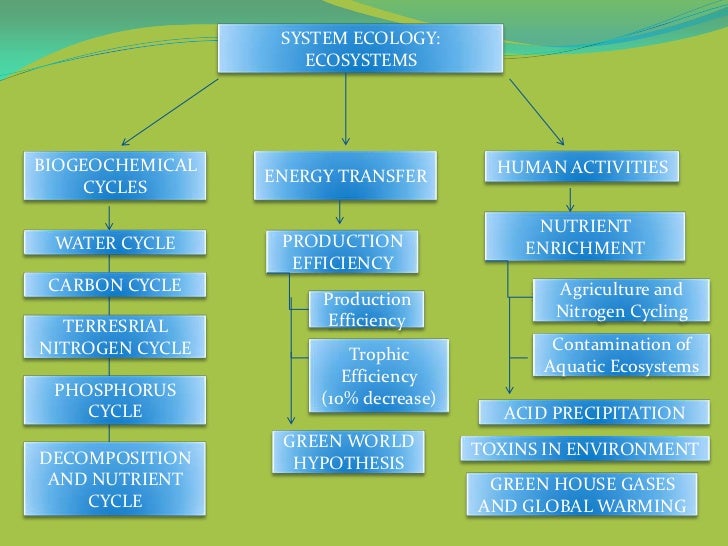



Ecosystems Concept Map By Grp 6
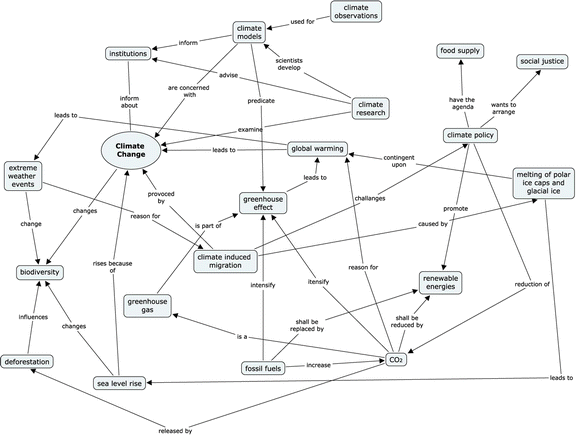



Supporting Students Learning And Socioscientific Reasoning About Climate Change The Effect Of Computer Based Concept Mapping Scaffolds Springerlink




Bio Chapter Homework Flashcards Quizlet



Global Warming Marie Koesnodihardjo
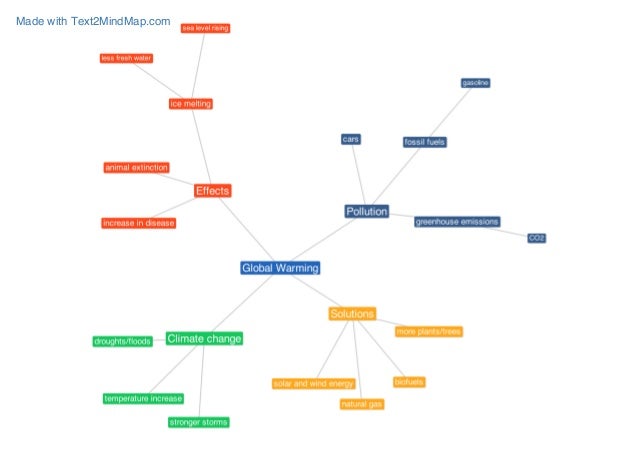



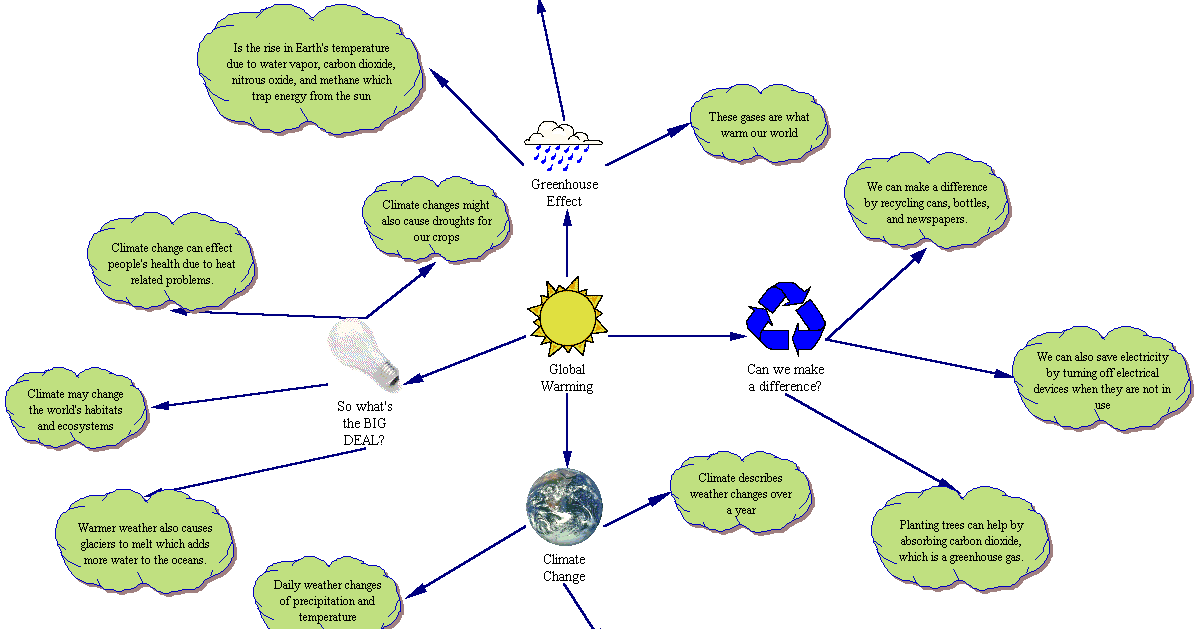
Concept Map Globalwarming
コメント
コメントを投稿